Table of Contents
ToggleAn Overview of Plastic Recycling
Recycling plastic wastes can lower the deposition rate of plastic trash, prevent plastic pollution, and thereby reduce the landfills’ dependence. Plastic recycling starts with recovering plastic waste and undergoing recycling measures to transform plastic waste into usable products.
Plastic waste recycling rates are increasing, but plastics production is far higher than the recycling rates. The usage of plastics has become more prevalent in the 21st Century; from toys to Smartphones, everything we own is made of plastic. Due to the growing economic growth, plastic recycling is becoming increasingly important.
Plastic recycling is necessary because all the existing plastic is non-biodegradable and will harm the environment for decades. The increase in plastic waste is due to multiple factors. The plastic recycling process also ensures that the large quantity of end-of-life plastic waste isn’t wasted but can be reconverted into a different usable one.
India’s Central pollution control board has passed several laws and regulations over the past several years to help state, district, and municipal governments efficiently handle plastic trash. However, plastic waste must be properly recycled at the proper recycling facility without harming the environment.
Did you know that plastics are one of the fastest-growing waste streams in the world today?
Check out this article to know about the various types of plastics, examples of standard products that contain them, what they’re used for, where you can find plastic recycling centres in your area, and how you can responsibly dispose of them to keep our planet green.
Stages involved in the Plastic recycling process
The plastic recycling process is carried out based on the type, class, and category of the plastic it belongs to, and the density of the plastic composition added. Therefore, effective plastic waste management activities need higher plastic recycling rates which can be achieved by the below-mentioned stages involved in recycling the plastic wastes. From collection to reprocessing, plastic wastes are transferred to multiple treatment stages.
Plastic waste Collection
The Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) are responsible for collecting plastic waste from residential, commercial, institutional, and other sources. Plastic waste collection is the major problem faced by rag pickers and ULBs, as there is no systematic approach to streamlining the door-to-door waste collection process.
Storage & Consumerization
All the collected plastic wastes need facilities or hubs for storage purposes. There are several ways to store plastic waste. First, plastic is often stored in denser forms, such as plastic pellets or special containers. These types of storage facilities will provide enough structural integrity to hold the weight of the waste.
Why plastic recycling is important, and what are the challenges faced by the Industry?
The waste management workflow needs to employ effective plastic waste management and recycling practices to eliminate plastic waste entirely from the environment. Plastics are everywhere to treat, but the waste management policies and framework must be advanced to match the current plastic waste management problems.
Although dealing with the plastic waste recycling processes is not simple, there are environmental, social & sustainable consequences to plastic waste disposal & treatment habits. Currently, most consumers, brands, manufacturers, and business owners tend to recycle plastics, but the question is, are they recycling them with proper effective measures?
So why is plastic recycling so important? The problem with plastics is that they cannot be used or will not degrade after usage. Also, when entered into the waste zone, plastic gets dumped into the landfills, thereby littering the landscape, polluting the water bodies, and causing a major threat to aquatic life. This is a significant drawback & the primary reason to opt for recycling. Recycling reduces waste and helps prevent pollution from being dumped into landfills or forgotten in rivers, lakes, and oceans.
As one of the essential products in the 21st Century, plastic poses a great problem when it becomes waste. Plastic recycling has many challenges in recycling and delivering the end product. Some of the difficulties faced by the recycling industry are,
Infrastructure
Many plastic recycling hubs are not equipped with machinery for automating the recycling process. Most of the Recycling hubs still follow the manual sorting and segregation process, which makes the process slow down. This process can also cause waste generation within the recycling system.
Lack of plastic waste segregation at source
To facilitate recycling operations, not only plastic waste but all waste must be sorted and segregated at the source. Therefore, the recycling process will be delayed unless plastic waste is segregated at the source. In addition, plastic waste will be mixed with non-recyclables, making the process more difficult and time-consuming.
Challenges in demand & Supply
Lack of awareness, poor compensation, and social status have created barriers to recycling plastic waste by expertise. The waste pickers have to struggle in collecting plastic wastes for low remuneration value, which makes them ignore managing particular plastic wastes due to low compensation value.
To overcome the demand & supply issue, CercleX has launched their digital platform “ScrapMarket” for traders, aggregators, and recyclers to buy & sell scraps across India with 100% verified buyers & sellers of paper, plastic, and metal scraps.
Types of Recycling techniques
Every day, plastic waste is recycled using a variety of techniques. The primary goal of recycling is to repurpose plastic again and again. However, plastic waste has been treated differently by many recycling facilities. In the past, plastics were recycled in the manual process, also known as traditional recycling treatment, and now the recycling of plastics is automated (Advanced recycling method).
Traditional Recycling technique
There are multiple ways to recycle plastic waste and prevent the plastic from becoming waste. The traditional recycling process is a multi-layer step-by-step treatment to handle plastic waste effectively.
Recycling plastic waste with traditional recycling directly replaces virgin materials in the production process to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water & soil pollution, and the generation of solid waste. Recycled thermoplastic materials are remelted or reprocessed into new products using injection moulding or extrusion. Traditional recycling techniques involve sorting, shredding, bailing, and processing plastic waste in a mechanical or manual process that consumes more time and is less effective.
Micro-plastic waste can be recycled through traditional recycling. It is recommended that microplastics be separated from other materials. Traditional recycling methods are eco-friendly to the environment.
Advanced recycling technique
With the power of science & technology, advanced recycling techniques have paved the way for recycling plastic waste again and again without dumping them into the garbage. The advanced recycling process transforms hard-to-recycle or non-recyclables into raw materials with effective recycling methodologies.
Advanced recycling is the process of converting more types of plastics into lower-volume products. We are all committed to natural and sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic manufacturing methods. We solve supply chain challenges by developing new materials and strengthening existing processes to help grow your business.
Plastics entering the environment are growing at an alarming rate. The advanced recycling process can take most plastics and return them to use once more. Products created with recycled plastic can be used in countless applications while addressing environmental concerns.
Processes involved in plastic recycling
Plastic recycling involves multiple stages. However, the process can be classified into several steps that are described below.
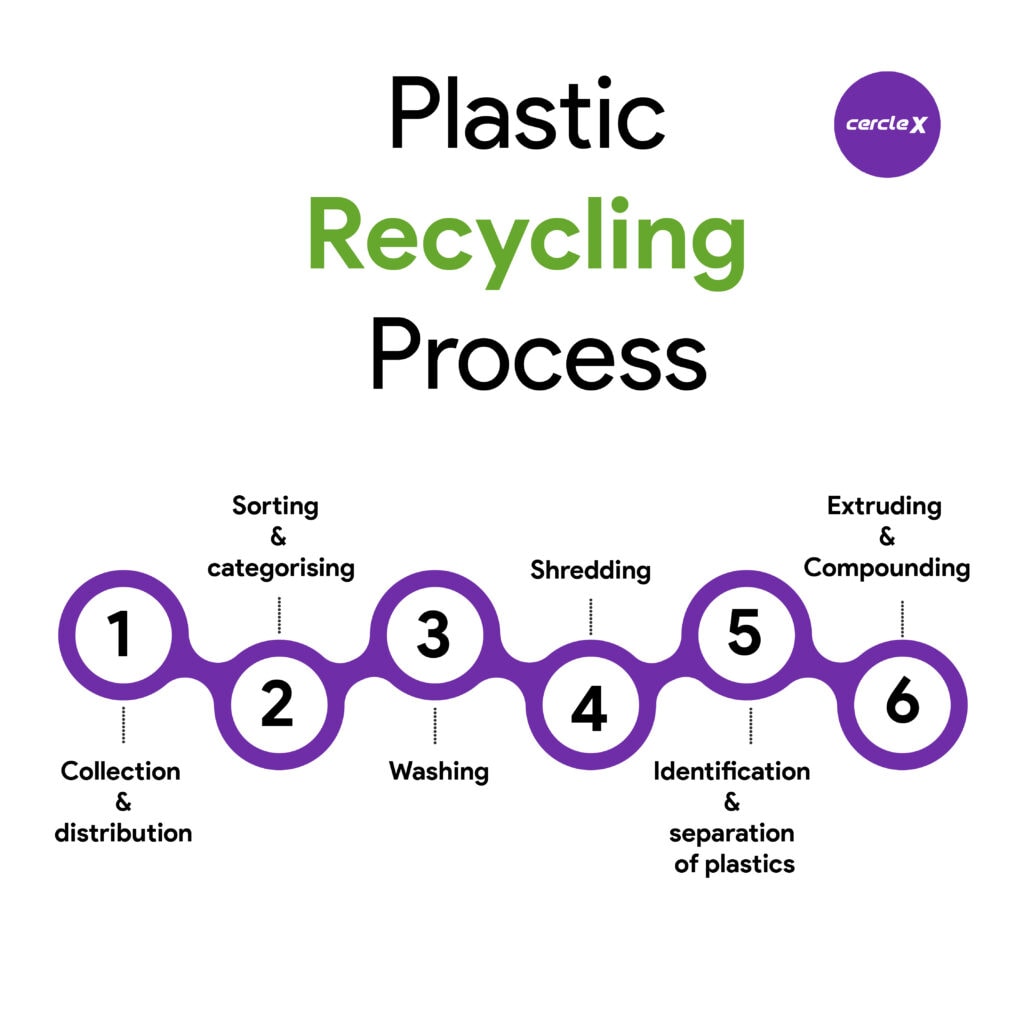
Collection & Distribution
Proper collection of plastic waste is the first step of the recycling process. The plastic recycling process involves collecting household plastic at home, in commercials, in residential areas, in schools, institutions, and at industrial business levels.
The raw plastic material is sorted and then sent to a recycling facility, which is processed into new products. The plastic waste collection includes everything from plastic bottles, paper, and cardboard to metal tins, glass, and plastic containers.
There are various ways to dispose of your plastic waste. For example, you can take plastic to community-run recycling collections (such as bottle banks or drop-off points) or bring it to a community waste site with large areas set aside for various recyclable materials.
Sorting & Categorising
Sorting and categorising is the process that follows the collection & distribution process in plastic recycling. Sorting involves differentiating or separating different types, classes, and grades of plastic and identifying recyclables and non-recyclable plastics by the recycler.
Also, the plastics collected by the ULBs needed to be differentiated in terms of use case, colour, thickness, and composition mixture level. Therefore, sorting and categorization is a significant process that directly results in the quality of the end product of recycled plastics.
Washing
Washing is another crucial step in the plastic recycling process. Washing is the key to getting plastic ready for recycling. This process removes impurities that can impede the operation or completely ruin a batch of recycled plastic. Even though plastics are often washed at this stage, it is important to ensure they are as free of impurities as possible before disposal or collection.
Washing off the sorted plastics increases the quality of the plastic pellet end product. In addition, sorting and washing the plastics without losing quality makes the pellets more consistent and less likely to break down over time, impacting their grade.
Shredding
After washing off the sorted plastics, the plastic waste enters the shredding stage. Shredding breaks plastic waste into smaller fragments for an easy repurposing process.
The plastic pieces have a much higher value than if they are thrown out as scrap, so the plastics can be utilized in other applications without further processing but sold directly as raw material.
The resizing process allows for the cleaning of plastic while preserving the integrity of the plastic material. In addition, these contaminants can be easily detected and removed during this manufacturing stage.
Identification & Separation of plastics
Once the plastics are sorted out & shredded into smaller pieces, the small plastic pieces are kept under quality testing or the Identification & separation process. In Identification & separation process, the small plastic pieces are classified based on their density, class, and quality grade.
The plastic density is tested by assembling the plastic pieces to float on a water container. The density test is a critical part of our process. The plastic particles are poured into a water container, and the results are determined. Knowing which pieces float means the specific plastic will be treated more efficiently because it will not be thrown away but somewhat recycled.
The thickness of plastics is tested by “Air Separation.” In this treatment, the plastic particles are kept in a wind funnel in which the thinner plastic particles get blown away, and only the thicker particles stay. The Air separation process determines the thickness of the shredded plastic particles.
Extruding & Compounding
The plastic goes from shredded up and crushed into a pellet of usable material. This is the last process; manufacturers can use it to make new plastic products. In addition, extruding & compounding refine the quality of the plastics for other operations.
Now the plastic is ready for manufacturers. First, it is melted and crushed together to form pellets. From here, the pellets are sent through a cooling process that slows down the reactions in the end product. This final cooling step helps reduce friction, which allows for more efficient manufacturing of our products.
Different types of plastics
There are over 50+ plastic categories in different grades, sizes, forms, and compositions. First, let’s check out some of the recyclable plastics.
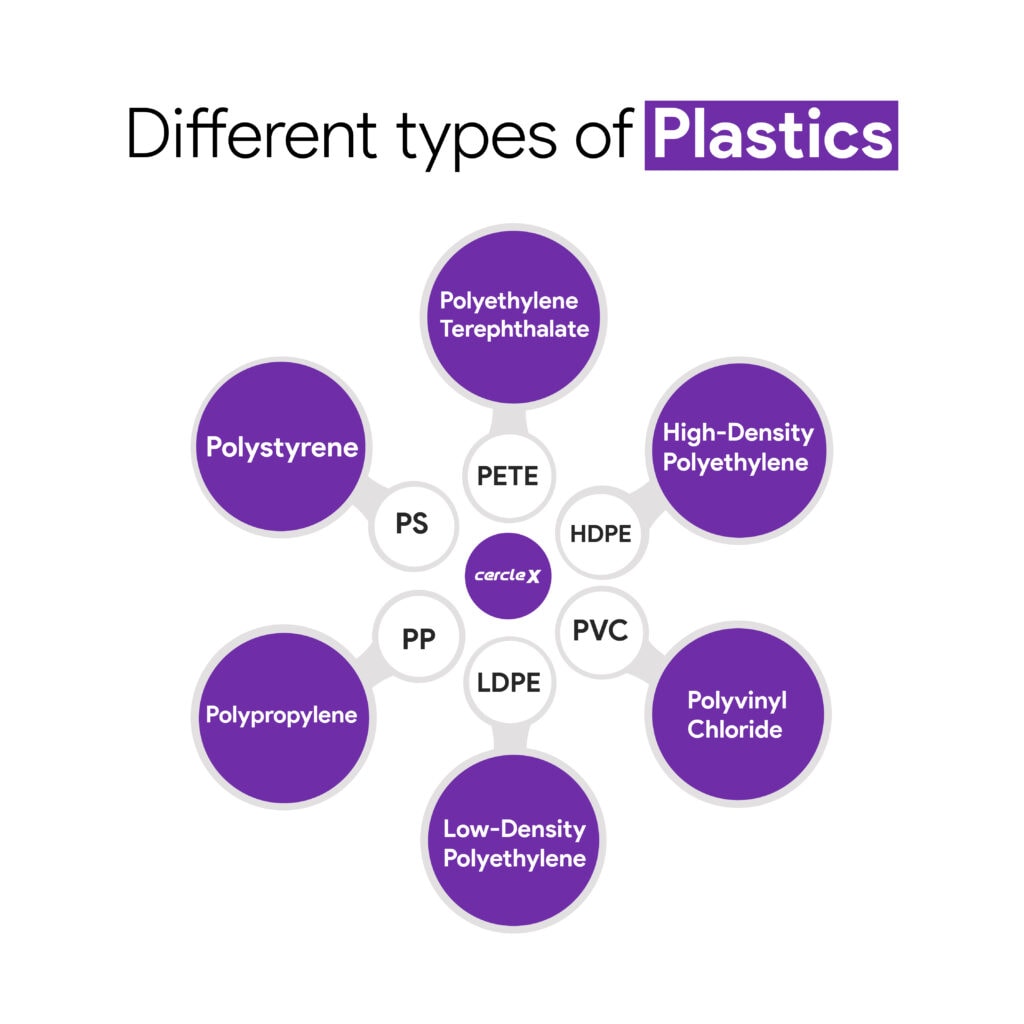
PETE (or PET) – Polyethylene Terephthalate
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is a common type of plastic known for its resistive property. As a result, PET is the most widely used plastic in the packaging, textile, and film industries.
PET offers excellent dimensional stability and transparency in printed patterns and flat or glossy printing. PET is also highly resistant to impact, moisture, alcohol, and solvents. PET is also a widely recycled plastic category.
HDPE – High-Density Polyethylene
HDPE (High-density polyethylene) is a petroleum-made thermoplastic polymer. HDPE plastic is used in many household products and industrial applications for heavy plastics. For example, HDPE plastics are widely used in plastic bottles, cardboards, cutting boards, and PVC piping applications.
HDPE plastics are known for their high-density tensile strength, rigidness, and durability and possess a high impact on resistance and melting point. In addition, after PET, HDPE types plastics are widely recycled across facilities.
PVC – Polyvinyl Chloride
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride), the white and brittle thermoplastic polymer, is one of the most widely used plastics worldwide. As its name indicates, VC has several properties based on the chemical composition of chlorine and vinyl chloride monomer units. These properties include high stiffness and strength at high temperatures, as well as good heat resistance and weather ability.
PVC is used in the classification of plastic manufacturing applications like floorings, signage, heavy plastic objects, and piping operations.
LDPE – Low-Density Polyethylene
LDPE (Low-density polyethylene) is a soft, lightweight, highly flexible plastic used widely in plastic manufacturing for plastic foams and sheets. LDPE has an excellent low-density value (0.9 g/cm³), good tear strength, bending strength, and resistance to abrasion, heat, aging, and corrosion.
LDPE is used to manufacture foams, food packaging films, and printed circuit boards. Low-density polyethylene – is a type of plastic that is easy to repurpose again and again.
PP – Polypropylene
Polypropylene is a polymer that is widely used in engineering applications. It provides strength and high impact resistance, particularly for blow-moulding bottles. The difference between PP and PAPER (sometimes known as Paperboard) lies in the structure or production process used.
PS – Polystyrene
Polystyrene (also known as Styrofoam) is a lightweight, solid plastic that can be moulded into many shapes. Plastics are made from petroleum, natural gas, chlorinated solvents, or ethylene chlorohydrin. Polystyrene foam is also a commonly used insulation material. In addition, it has been used to make soundboards for guitars, guitar picks, and other musical instruments.
Facts & Figures on plastic recycling
In our world, plastic seems to be everywhere. Around 6.3 billion metric tons of plastic have been wasted in the last 70 years, totalling 8.3 billion metric tons. Only 9% of that waste is recycled.
Seventy per cent of plastic waste in India is recycled at Registered Offices, 20 per cent by the Unorganized Sector, and 10 per cent by individuals at home. However, more than 100 billion plastic bottles are produced yearly, of which only 35 billion are recovered and recycled.
In recent years, plastics have become ingrained in our lives. We use plastic materials to pack our meals, store our food, build our homes and even treat medical conditions. However, these plastics are quickly becoming a significant problem – they can take up to 1,000 years to decompose, and some say they’ve even found plastic bags in the Arctic.
Do you know what the primary purpose of plastic manufacturing is?

Nearly 73% of the plastics are produced for “Packaging .”If the plastics are not used in the product design, they exist in the product’s packaging. A recent global energy and carbon accounting analysis study found that between 2.5% and 3.6% of worldwide oil and natural gas consumption was used as feedstock for plastic.
Plastic waste is a burden on our oceans and the environment. The problem of plastic pollution is not new, but it appears to worsen. The United Nations Environment Programme estimates that over 400 million metric tonnes of plastic waste are generated annually, with 88% ending up in landfills or oceans.
Many initiatives have sprung up worldwide to combat the problem, including reducing the use of disposable single-use items and making sure plastics are recycled. However, the recycling rate in India is slightly lower when compared to other countries, as there is no proper awareness of plastic recycling, and the informal sectors maintain more than 60% of plastic waste recycling.
Nature is slowly disappearing faster, and there is almost no use for plastic in our daily life. The resources we have today will not be available by ourselves, but keeping them safe is crucial. Recycling plastic helps in preserving one-third of the natural resources from being depleted. Recycling also ensures that plastic waste is correctly disposed of, reducing the environmental contamination.
Recycling is the only option left; bringing the unutilized resource back to usage is essential. Recycling plastic helps in preserving one-third of the natural resources from being depleted. It has several benefits and people around the world try their best to live a life and recycle everything they cannot use anymore.
Plastic recycling Industry Association
The PLASTICS Recycling Committee brings together and represents PLASTICS members across the association’s four councils, representing equipment makers, brand owners, processors, and material suppliers. The committee works to enhance the management of plastic waste through efforts such as advocating for increased collection, sortation, and recycling infrastructure, ensuring the definition of “recycling” includes advanced recycling, and much more.
The Association of Plastic Recyclers (APR)
Plastics are an important raw material for the production of various products. The country has several industries that are primarily based on Plastic consumption or Plastic Products. Hence, the Indian Plastics Industry has a large share in the production and consumption of plastics. The industry is an integral part of the overall economy because it contributes to investment, employment generation, and economic growth.
Currently, the Indian Plastics Industry is well positioned to take advantage of new market opportunities and introduce new technologies that can boost sustainable growth.
Plastic is a versatile material used in the production of everyday products, ranging from packaging and packaging materials to products that are consumed. The growing need for plastics has led to the increasing use of this resource.
In modern times, plastic materials have played an essential role in our everyday lives. However, there is also a high amount of plastic waste generated every day. This waste can be recycled, but it has become difficult due to a lack of awareness regarding its recyclability.
Plastic Recycling FAQs
Recycling plastic seems to have many undetermined sides that people and traders are unaware of. So let’s discuss a few key points on where plastic wastes are recycled, who & which brands & organisations recycle plastic, and where the collected plastic is deposited or stored for recycling. Also, we’ll clearly brief on what plastics are recyclable and non-recyclable plastics.
Which Companies and Organisations Collect and Recycle Plastic Waste?
Many companies & brands work on recycling plastic waste, recycling the plastics, and repurposing end-of-life plastic waste for future use again and again. CercleX is one of India’s top plastic waste recycling companies, aiming to digitize the waste management eco-space with technological advancements.
CercleX closely works with urban local authorities and partners to implement innovative solutions that help us tackle issues of waste segregation, collection, transportation, and recovery. CercleX is a one-stop solution for all your waste management needs, offering services such as Extended producer responsibility (EPR) and handling complete Industrial waste management (IWM) services, working with traders, aggregators & recyclers to buy & sell scraps online with the ScrapMarket application. CercleX serves cities across India and even abroad with the latest technology.
Where Can You Deposit Your Plastic Items?
Once the plastic waste collected for recycling has passed through different processing stages, it is sorted according to its size and quality before being shipped back to the consumers.
There are many stages of the plastic recycling process. The recycling system will be developed as an integral part of integrated solid waste management systems.
The plastic waste collected for recycling will be stored in the recycling facilities and hubs for multiple stages of plastic processing such as Collection & Consumerization, sorting & categorising, washing, shredding, bailing, bundling, melting & re-organizing, and then processing the plastic into smaller fragments to repurpose again.
How To Identify What To Recycle
Almost everyone knows what recycling is and how it works but we may not know that all plastics cannot be recycled; only some of the plastic categories can be recycled, and others not. To find recyclable plastics check out below.
Getting to the right answer about whether recycling is a problem includes understanding the processes that convert waste materials into new objects. Some environmental scientists say that recycling does not reduce emissions because it does nothing to reduce the number of materials being produced, just how those materials are used.
In contrast, some other researchers say that recycling reduces emissions, which is more effective than simply disposing of waste at landfills.
Conclusion
Plastic recycling is more important than ever in today’s world. With so many plastics available and used, it can be challenging to know which ones you can recycle and which you cannot. Plastics evolve in different types, specific properties and uses. The challenge is knowing which kind of plastic a particular item is made from, as that will determine whether or not it can be recycled.
Did you also know that plastic is one of the most unsustainable materials we use today?
That’s right, billions of bottles, containers and other plastic packaging items are thrown away yearly and end up as rubbish. That’s because plastics don’t biodegrade as other natural materials do. Instead, a minor plastic fragment can take up to a thousand years to break down into smaller pieces. But thanks to the rise in awareness about environmental issues, there has been a significant increase in plastic recycling programs throughout the world. Here’s why you need to learn how to recycle plastics if you haven’t already done so.
There are many critical environmental issues today. Even though, many people don’t take action and positively impact the world. Recycling is one of the most substantial things you can do to help reduce your carbon footprint.
Let’s try to keep our ecological footprint with Zero waste which we can take to future generations
